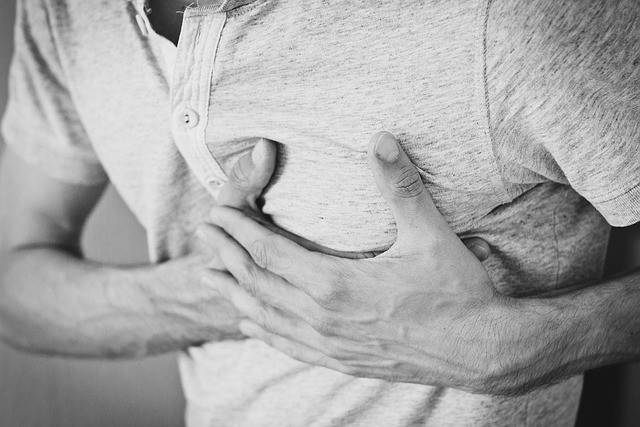
Chest tightness is a common symptom experienced by people with various lung conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and bronchitis.
Tightness can be described as a feeling of pressure, squeezing, or heaviness in the chest, which may cause discomfort and anxiety. Understanding what chest tightness is and how to manage it can greatly improve the quality of life for those living with lung conditions.
What causes chest tightness in lung conditions?
Chest tightness in lung conditions is often a result of inflammation and narrowing of the airways, making it difficult for air to move in and out of the lungs. Some common triggers include:
- Allergens (pollen, dust mites, pet dander)
- Irritants (smoke, pollution, strong odors)
- Respiratory infections
- Cold air
- Exercise
- Stress and anxiety
Ways to relieve and reduce chest tightness:
Use prescribed medications: Follow your doctor’s instructions for using inhaled bronchodilators (e.g., albuterol) or corticosteroids to open up the airways and reduce inflammation.
Practice breathing techniques: Deep breathing, pursed-lip breathing, and diaphragmatic breathing can help control breathing and alleviate chest tightness.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight can help improve lung function and reduce the frequency of chest tightness episodes.
- Engage in low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling to improve lung capacity and overall fitness.
- Follow a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to support lung health.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on your lungs and improve breathing.
Avoid triggers: Identify and avoid triggers that worsen your chest tightness, such as allergens, irritants, or extreme temperatures.
Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or hobbies to help relax and prevent stress-induced chest tightness. By managing stress through relaxation techniques and seeking support from loved ones or mental health professionals, you can better cope with the psychological effects of your condition.
Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help thin mucus and make it easier to clear your airways.
Use a humidifier: Using a humidifier can help soothe irritated airways and reduce chest tightness, especially in dry environments.
In Summary…
It’s crucial to work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized action plan for managing chest tightness episodes. If you experience severe shortness of breath, chest pain, or blue lips or fingernails, seek emergency medical care immediately.
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor your lung health and adjust your treatment plan as needed. By staying proactive and informed about your condition, you can better manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.