If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with a long-term lung condition then you may have heard about the importance of monitoring oxygen saturation levels. In this blog post, we’ll explain what oxygen saturation is, how it’s measured, and why it’s crucial for managing these conditions.
What Is Oxygen Saturation
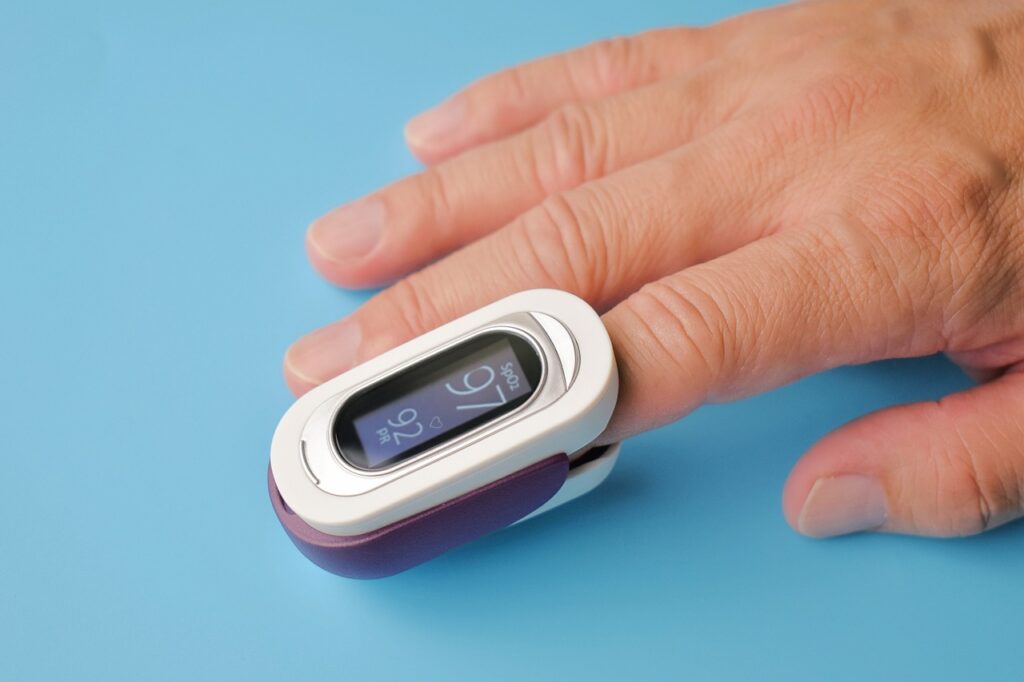
Oxygen saturation, often referred to as SpO2, is a measure of the amount of oxygen carried by red blood cells in the body. It is expressed as a percentage, with normal levels typically ranging between 95% and 99%. When oxygen saturation levels fall below 90%, it is considered a cause for concern and may indicate that the body is not receiving enough oxygen.
How is Oxygen Saturation Measured?
Oxygen saturation levels can be easily measured using a small device called a pulse oximeter. This non-invasive tool is placed on a finger, toe, or earlobe and uses light to measure the amount of oxygen in the blood. The device is painless and provides a quick reading of your oxygen saturation level.

Why is Oxygen Saturation Important for People with Lung Conditions?
For individuals with lung conditions, monitoring oxygen saturation levels is crucial because these conditions can cause a decrease in the amount of oxygen that reaches the bloodstream. As these diseases progress, the lungs become less efficient at exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide, leading to lower oxygen saturation levels.
Low oxygen saturation can have various negative effects on the body, including:
- Increased strain on the heart
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Confusion and disorientation
- In severe cases, organ damage or failure
Monitoring oxygen saturation levels allows people with lung conditions to track their condition and make necessary adjustments to their treatment plan. If levels consistently fall below 90%, it may be necessary to use supplemental oxygen therapy to maintain adequate oxygenation and prevent complications.
Tips for Maintaining Healthy Oxygen Saturation Levels
- Quit smoking, as it can further damage the lungs and reduce oxygen intake
- Engage in regular physical activity, as prescribed by your healthcare provider, to improve lung function
- Use prescribed medications, such as bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids, to manage symptoms and improve airflow
- Attend pulmonary rehabilitation to learn breathing techniques and strategies for managing your condition
- Use supplemental oxygen as directed by your healthcare provider
Final Words
In conclusion, understanding and monitoring oxygen saturation levels is essential for people living with lung conditions. By working closely with your healthcare team and taking proactive steps to manage your condition, you can maintain healthy oxygen levels and improve your overall quality of life.