If you have a chronic lung condition such as COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) or emphysema, monitoring your blood oxygen levels is crucial for managing your health. Blood oxygen levels indicate how well your lungs are functioning and delivering oxygen to your body. In this blog post, we’ll explore what blood oxygen numbers mean and why they matter.
What are blood oxygen levels?
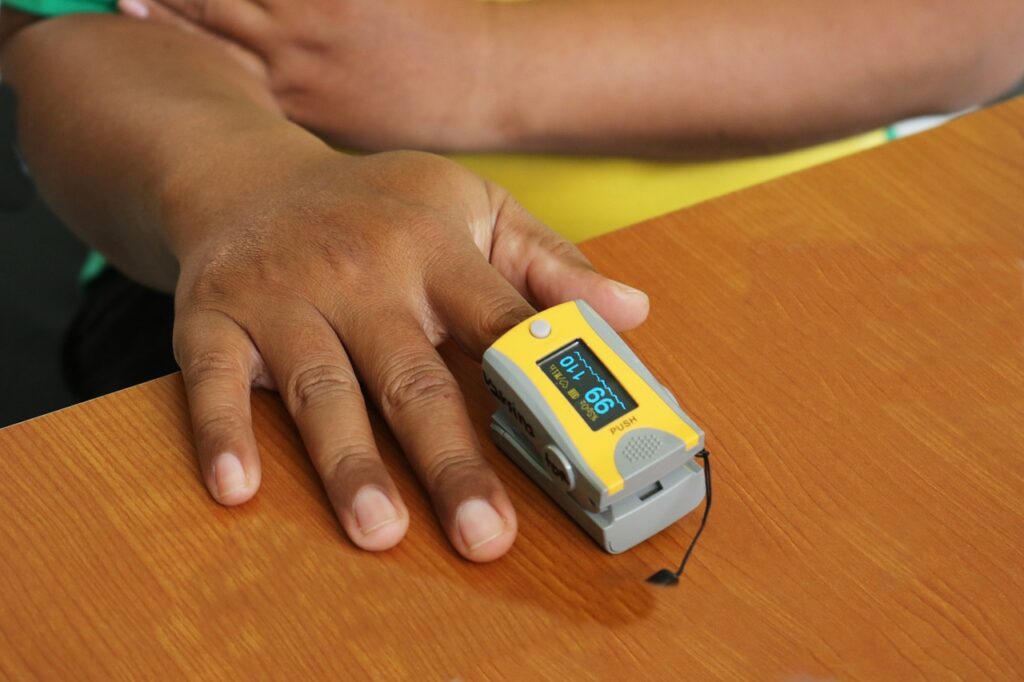
Blood oxygen levels, also known as oxygen saturation, refer to the amount of oxygen circulating in your bloodstream. This is usually measured as a percentage, with a normal range typically between 95% and 100%. If your blood oxygen levels fall below 90%, it may be a cause for concern and require medical attention.
How are blood oxygen levels measured?

The most common way to measure blood oxygen levels is through a pulse oximeter, a small device that clips onto your finger, toe, or earlobe. It uses light to measure the amount of oxygen in your blood, providing a quick and non-invasive reading. Your healthcare provider may also perform an arterial blood gas (ABG) test for a more accurate measurement.
Why are blood oxygen levels important for COPD and emphysema patients?
COPD and emphysema are progressive lung diseases that cause airflow obstruction and difficulty breathing. As these conditions worsen, the lungs become less efficient at transferring oxygen into the bloodstream. Low blood oxygen levels (hypoxemia) can lead to various health problems, including:
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid heartbeat
- Fatigue and weakness
- Headaches
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
- In severe cases, organ damage or failure
Monitoring blood oxygen levels helps you and your healthcare team assess the severity of your condition and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
What can you do to maintain healthy blood oxygen levels?
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a leading cause of COPD and emphysema and can further damage your lungs, making it harder to maintain adequate blood oxygen levels.
- Use prescribed oxygen therapy: If your blood oxygen levels are consistently low, your doctor may prescribe supplemental oxygen to help you breathe easier and protect your health.
- Practice breathing techniques: Techniques like pursed-lip breathing and diaphragmatic breathing can help you breathe more efficiently and improve oxygen intake.
- Stay active: Regular exercise, as tolerated and approved by your doctor, can help improve lung function and circulation.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet and maintaining a healthy weight can support overall lung health and oxygenation.
Final Words
If you have COPD, emphysema, or another chronic lung condition, work closely with your healthcare team to monitor your blood oxygen levels and develop an appropriate treatment plan. By staying informed and proactive about your health, you can better manage your condition and maintain a good quality of life.